Although in modern times, we like to pride ourselves on the amount of history that we know about humankind, we still only know a small fraction. Every day, new discoveries are being made that prove we aren’t as knowledgeable as we once thought, and give us more insight into the past that is still a complete mystery in any aspect.
Take a look at these more recent discoveries that prove we have only scratched the surface about understanding our ancestors.
A Mask That Isn’t For Wearing
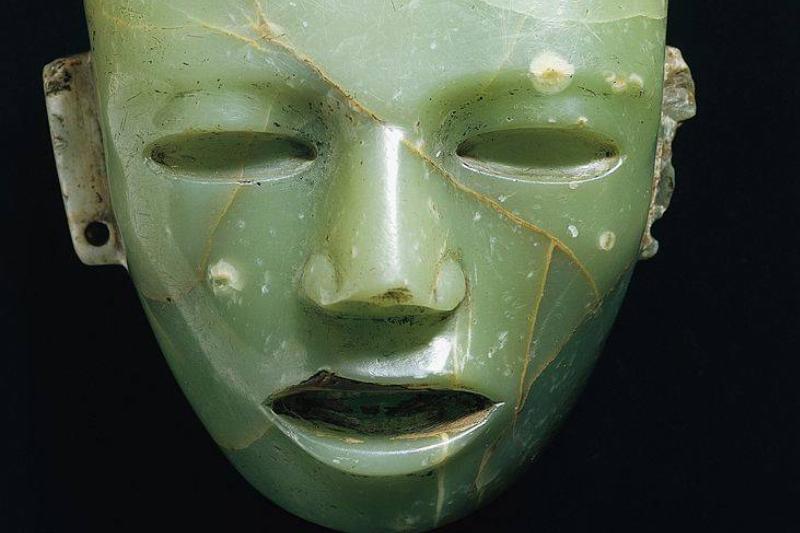

This interesting green mask was discovered at the base of a pyramid in Mexico in 2011 and assumed to have been placed in the ground as an offering to the gods around 2,000 years ago.
Along with the mask, archeologists also found pieces of obsidian and pottery made from the same material of the green stone. It is believed that the mask was not made for wearing but was part of a dedication ceremony, and is most likely made in somebody’s likeness, which gives researchers a glimpse into what these people look like.
ADVERTISEMENT
An Abandoned Train In The Desert
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
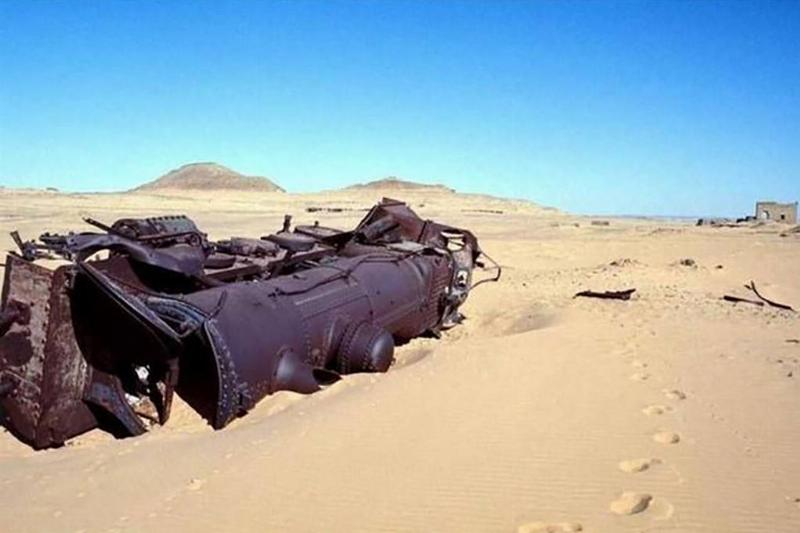
To many, this may just seem like a train buried in the desert sand, but this is actually the evidence of a feat accomplished by T.E. Lawrence during World War I. In 1917, Lawrence was serving in the Middle East, where he and a band of Arab followers began attacking Ottoman supply trains.
ADVERTISEMENT
By the end of the war, Lawrence and his comrades had destroyed so many trains that the railroad could no longer be used. Furthermore, rather than cleaning up the trains, the Turkish people just left them in the desert.
ADVERTISEMENT
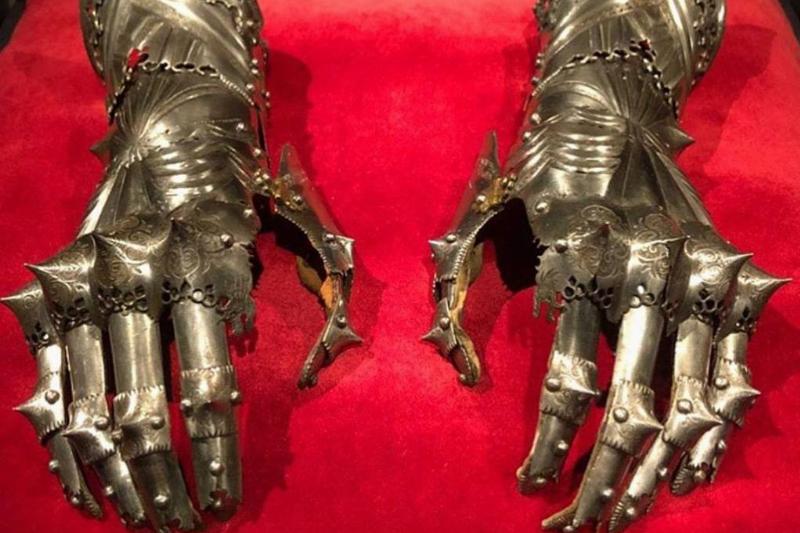
No Ordinary Gloves
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
These gloves are known as gauntlets and were a type of glove that was worn by soldiers and knights during the Middle Ages. Although they could be used for decoration, they were also designed to protect the wearer’s forearms and hands during combat.
ADVERTISEMENT
However, these are no ordinary gauntlets. Experts believed these were the gloves of the Holy Roman Emperor Maximillian I. Supposedly, Maximilian I wore these gloves for the majority of his life up until his death in 1519.
ADVERTISEMENT
Primitive Snow Goggles
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
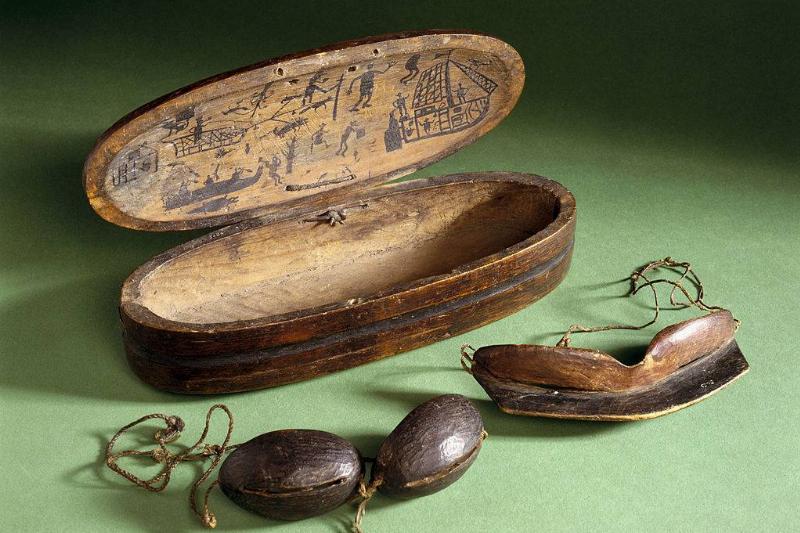
The sun has had negative effects on the human eyes since the dawn of man. However, the ancient people, such as the Inuits, created ways to lessen the effects of the sun.
ADVERTISEMENT
For example, more than 2,000 years ago, when the Inuit people would travel across the snow, they hand-carved snow goggles, making little slits that provided enough vision. Researches are impressed by these goggles because they don’t fog over in the polar conditions, which is an issue people still face today.
ADVERTISEMENT
Not Just A Rock
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
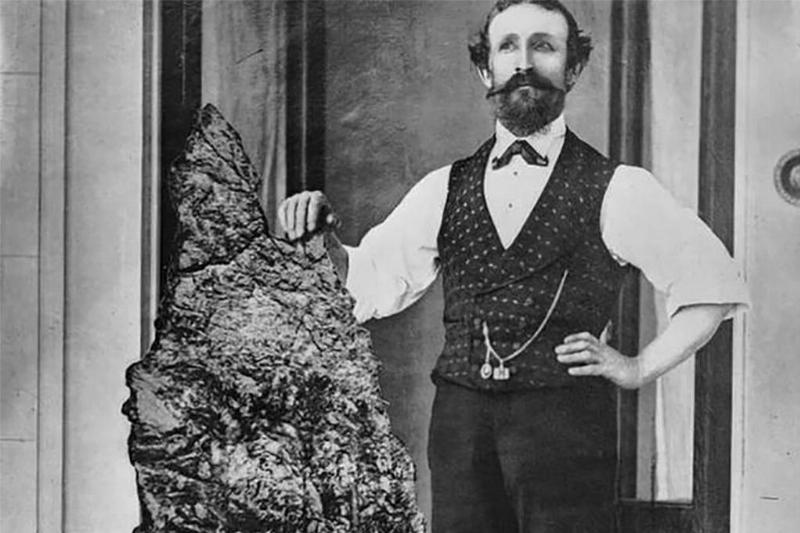
Here, it may seem that this is a man taking a picture next to a rock, but this couldn’t be further from the truth. Pictured, in Bernhardt Otto Holtermann, who owned part of an Australian mine where veins of gold were discovered. Here he is next to a giant golden nugget that was discovered on his land.
ADVERTISEMENT
This photo was taken by an unknown photographer before Holtermann was elected as a member of St Leonard’s parliament in 1882. Unfortunately, he died in a premature exposition of blasting powder at the age of 47.
ADVERTISEMENT
A Watch Fit For A Queen
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
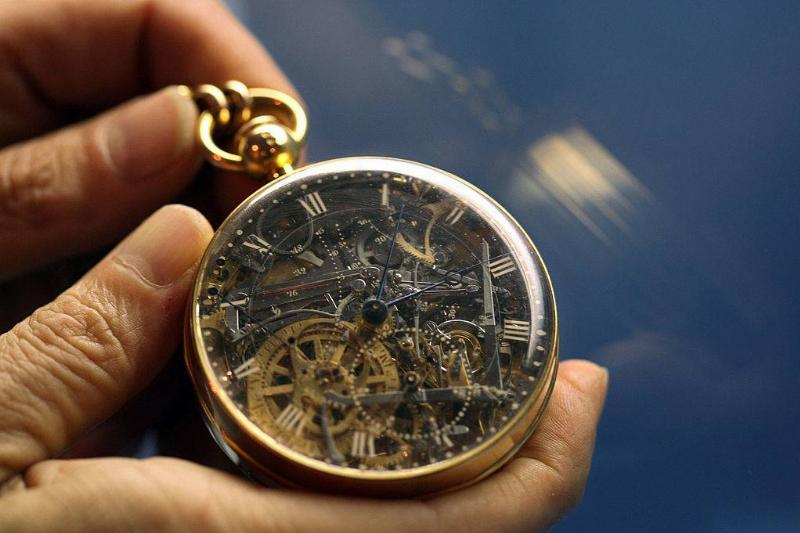
This incredibly ornate pocket watch turns out to have been commissioned for Marie Antoinette by a mystery suitor in 1783. Clearly, no expense was spared, and the gold and other materials that were used are assumed to be worth $30 million.
ADVERTISEMENT
The watch is one of a kind and includes a full calendar, an hour jumping hand, 23 complications, and 823 individual parts. It is considered to be the fifth most intricate watch ever made, although unfortunately, Antoinette never received it as she had been executed before it was completed.
ADVERTISEMENT
This Statue Tells A Story
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
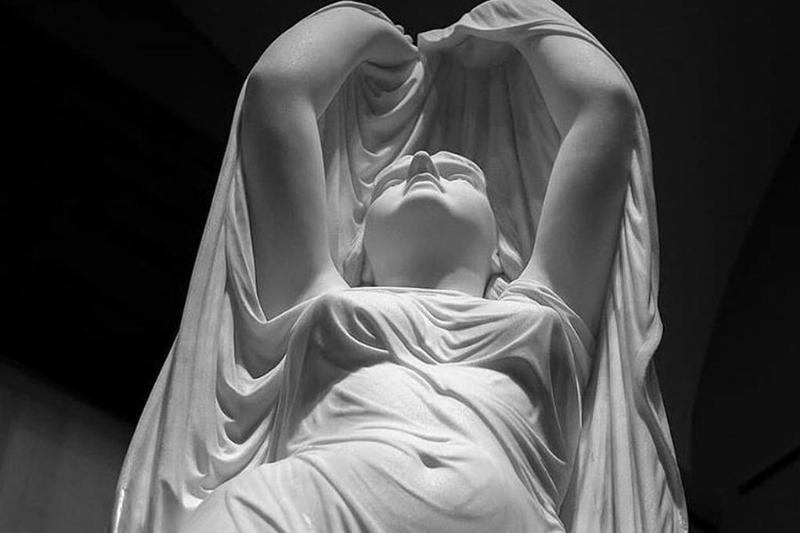
This statue was created by 19th-century American artist Chauncey Bradley Ive, and is a representation of the mythological Mediterranean sea spirits known as Undines. Stories about Undines became popular after the release of the novel Undine, written by Baron Heinrich Karl de la Motte Fouqué.
ADVERTISEMENT
The story follows an Undine that takes on a human form to marry a knight. However, after he is unfaithful, she is then forced to kill him. This statue shows the Undine coming out of the water.
ADVERTISEMENT
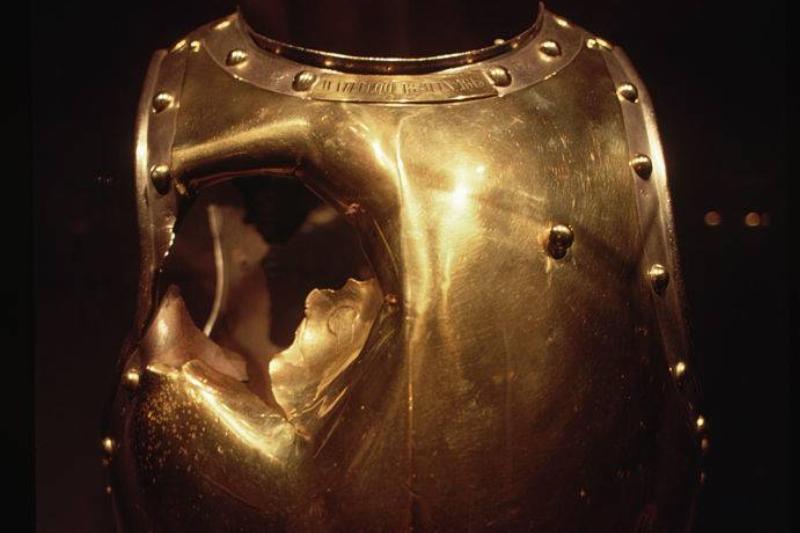
The Horrors Of War
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Serving under Napoleon during one of the battles at Waterloo, Antoine Fraveau was a 23-year-old cuirassier that donned this breastplate before taking to the field of battle. This was an important piece of armor because it protected against swords, other weapons, and at times even bullets.
ADVERTISEMENT
However, one thing it couldn’t protect against was cannon fire. While fighting in 1815, Fraveau was killed after being hit by direct cannon fire. Unfortunately, he was supposed to get married not long after. This perfectly shows the violence of warfare back then.
ADVERTISEMENT
A Statue That Isn’t All It Seems
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
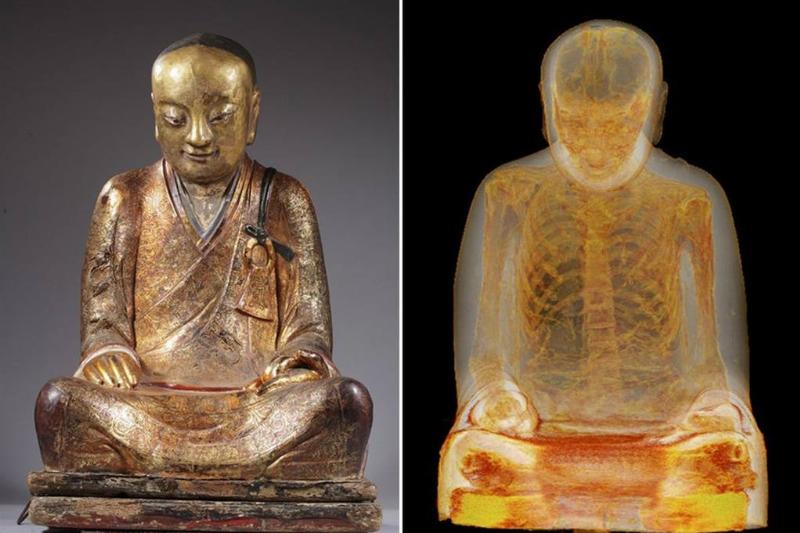
Back in 2015, researchers in the Netherlands performed a CT scan on a statue of a Buddha, and they never expected what they would find inside. Inside of the statue, it was discovered that it contained a mummified monk that had been entombed for over 1,000 years.
ADVERTISEMENT
Incredibly, rather than placing the monk inside of the statue, researchers found that the monk was filled with scraps of papers covered in Chinese characters. Incredibly for a monk to be mummified, they would drink a poisonous tea to ensure that their body would be too toxic to be consumed by maggots.
ADVERTISEMENT
Royal Sandals
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
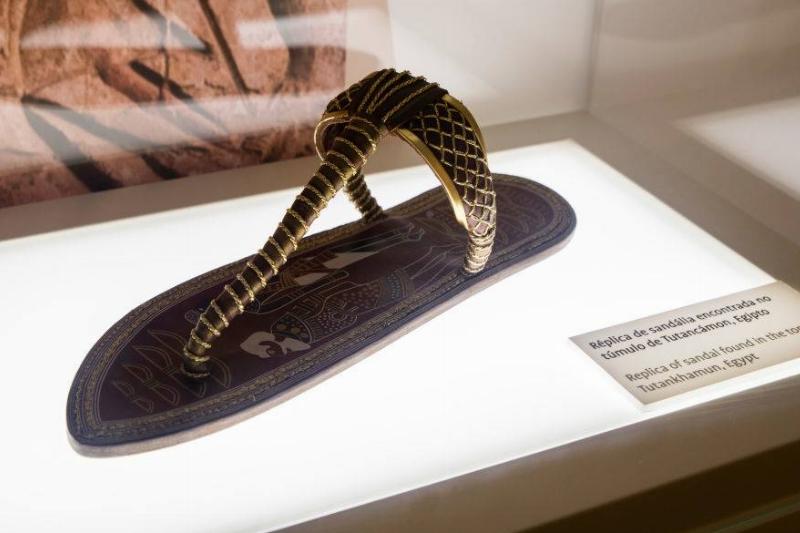
When most people think about Egypt, they think about mummies, great pyramids, and fancy eyeliner. However, these sandals worn by King Tut show that the people in Ancient Egypt were more modern than most might expect.
ADVERTISEMENT
Apparently, they were just as into fashion as modern-day humans, with ancient footwear expert, André Veldmeije, noting, “When footwear is mentioned in general books, if at all, it is usually noted that sandals were flimsy and most people were barefoot all the time. Moreover, they say there were only few types of sandals. This is a misconception, probably based on artistic depictions alone.”
ADVERTISEMENT
The Missing Pilot
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
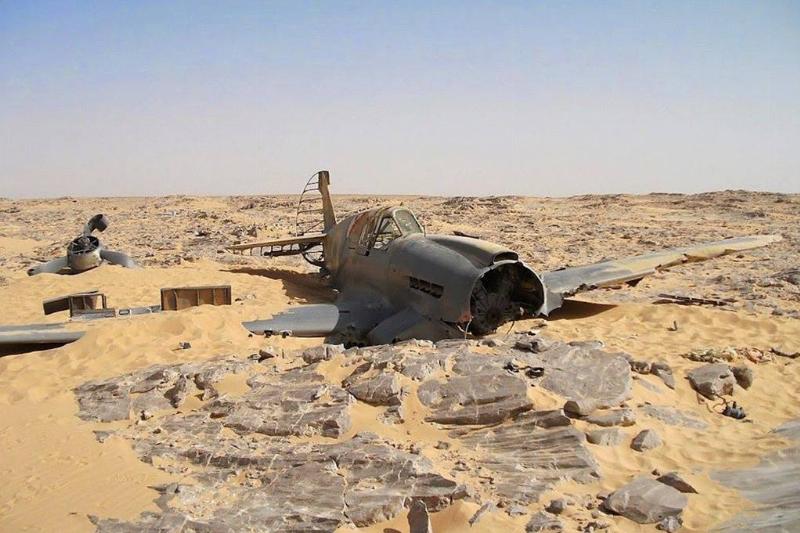
Here is a Curtiss P-40 Kitty Hawk, which was a British version of the American Tomahawk that was used during World War II. With a range of only 240 miles, the plane was typically just used as a defensive craft.
ADVERTISEMENT
This particular plane was found in the Sahara Desert in 2012. It was piloted by 24-year-old Flt Sgt Dennis Copping, who went down in the North African desert in June 1942. The plane remained undisturbed until it was discovered by an oil company worker in 2012, although nobody knows what happened to the pilot.
ADVERTISEMENT
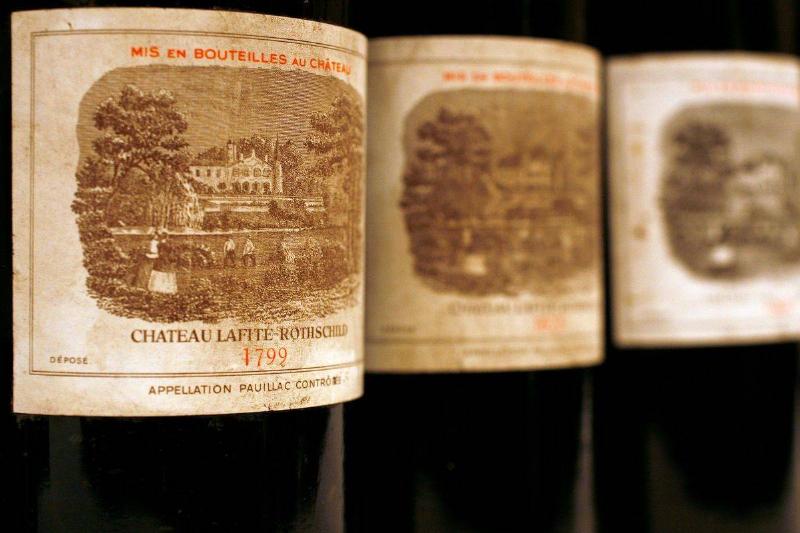
141-Year-Old Wine As A Reward
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
Following the events of September 11, 2001, Osama Bin Laden, the leader of the Taliban, became public enemy number one in the western world. Everyone wanted him caught and brought to justice, especially one restauranteur Ted Balestreri.
ADVERTISEMENT
The Californian claimed that he would open up his bottle of 141-year-of Chateau Lafite Rothschild with the US Defense Secretary if they helped bring Bin Laden down. After Bin Laden was killed in 2011, Balestreri said he’s happy to open up the bottle to celebrate.
ADVERTISEMENT
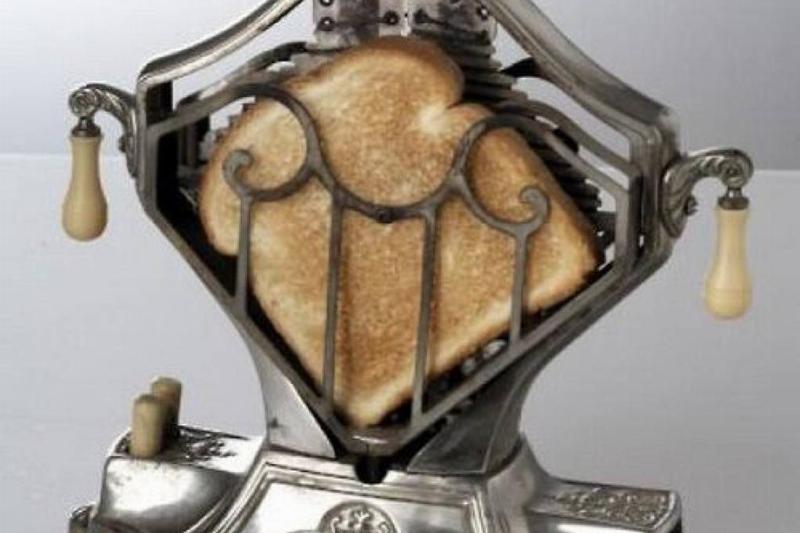
There Was Toast Before Toasters
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
Although most people today might throw a piece of bread in the toaster in order to make a piece of toast, that didn’t mean that people of the past didn’t enjoy a crisp piece of bread either.
ADVERTISEMENT
Here is an early version of a toaster, however, instead of toasting both sides, it only heats up one side at a time. So, when the user is happy with the toast of their bread, they would have to manually flip the bread to do the other side.
ADVERTISEMENT
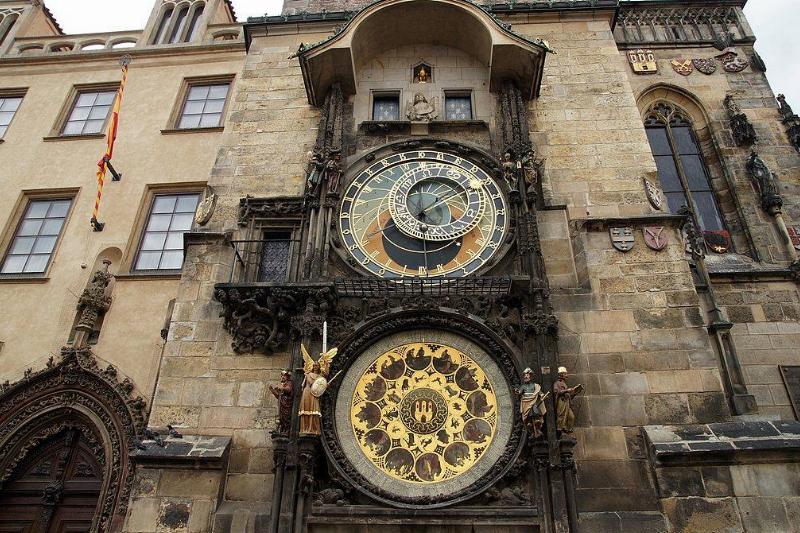
The Oldest Astronomical Clock
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
The Prague Astronomical Clock is one of the world’s oldest and fully functioning astronomical clocks, which tells the time as well as information about the sun, moon, zodiac constellations, and other plants.
ADVERTISEMENT
The clock in Prague is often referred to as The Orloj, and in order to be a fully functioning clock, it had to be constructed in multiple layers. The main face of the clock features the time as well as glyphs that show ancient Czech time, and Roman numerals for 24 hour time.
ADVERTISEMENT
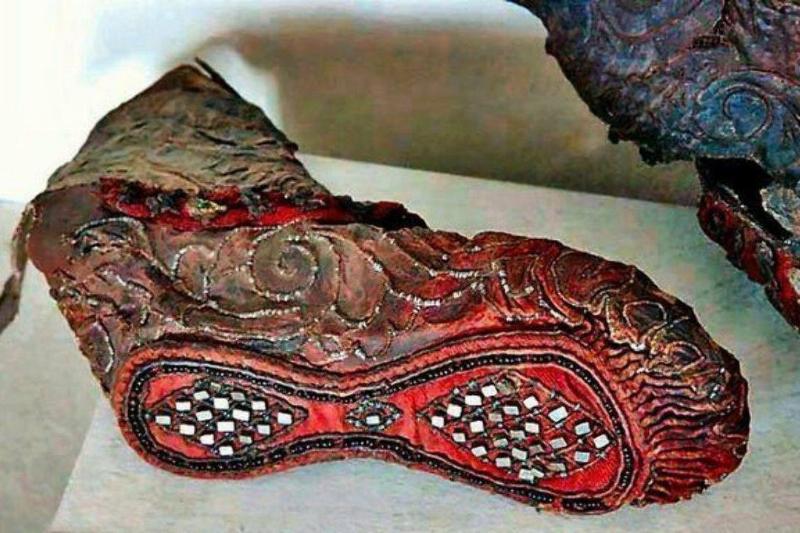
Frozen In Time
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
Although this might look like a typical ornamental shoe, it’s actually a preserved woman’s boot that dates back over 2,000 years ago. Incredibly, they remained almost completely preserved due to the freezing temperatures of the Altai Mountains.
ADVERTISEMENT
The boot dates back to 300 BC and is made of a variety of materials including pewter, pyrite, glass beads, gold foil, and more. Incredibly, even back then, people put a lot of effort into fashion, and the work shows.
ADVERTISEMENT
That’s Not Art
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
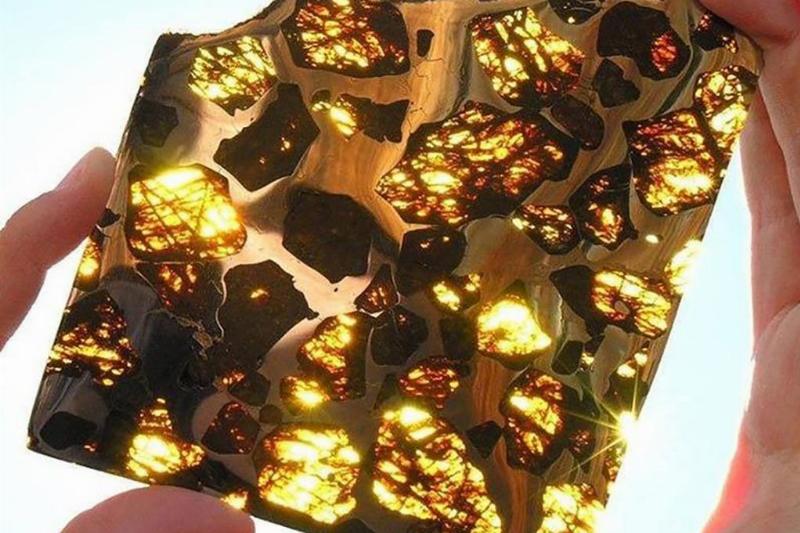
While this might look like a beautiful piece of glasswork, it’s actually from outer space. Discovered in Fuang in Xinjiang, a region of northwest China, this incredible rock is made up of a variety of materials including Pallasite, which is recognizable for its pieces of olive crystal that are embedded in a nickel-iron crystal.
ADVERTISEMENT
When light is shown through the back of a crystal, it looks like stained glass, but it’s actually a piece of meteorite. Scientists aren’t exactly sure of the origins of Pallasite, but they assume that the meteorite was formed around 4.5 billion years ago.
ADVERTISEMENT
Civil War Surgeon’s Kit
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
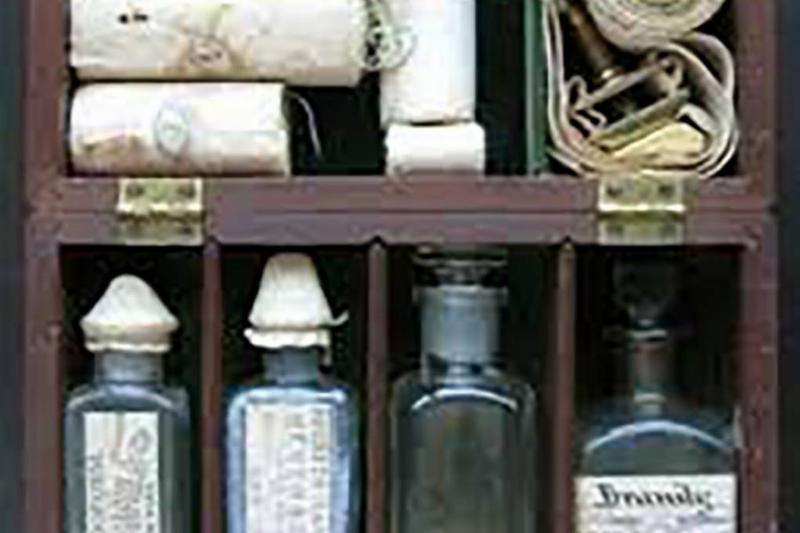
Since there have been violent conflicts, there have been those on the battlefield tending to the wounded. While they may not have the same equipment that we use today, here is what a pretty standard surgeons kit looked like during the American Civil War.
ADVERTISEMENT
It may not have been much, but it did help to save countless lives on the battlefield. We can be lucky that our medics today are a little more prepared.
ADVERTISEMENT
A Musical Typewriter
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
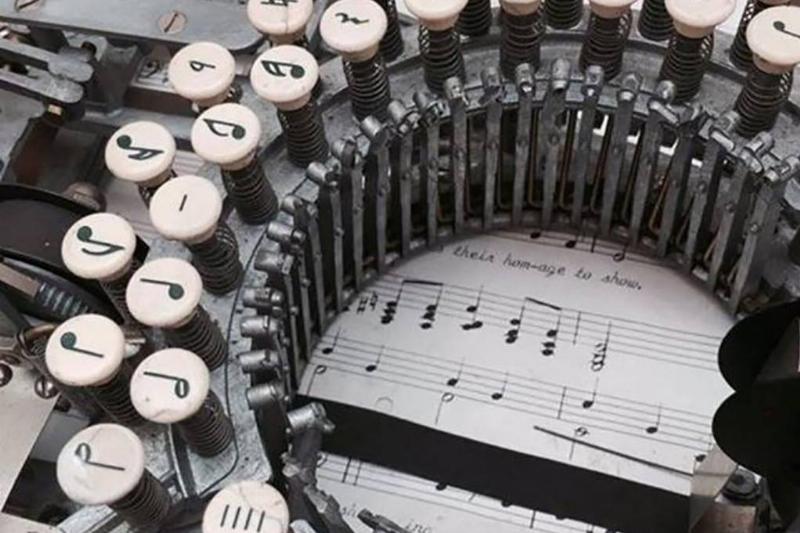
Although first patented in 1936, the Keaton Music Typewriter initially only had 14 keys, but by the 1950s, had an impressive 33. The machine worked by placing a sheet of paper beneath the typical mechanism before the notion marker started typing.
ADVERTISEMENT
Although the machine looks difficult to use, it proved to be efficient. Typewriting made writing sheet music easier, but the user had to work cautiously, or else they would have to start all over with a new sheet of paper.
ADVERTISEMENT
The Carriage With No Rider
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
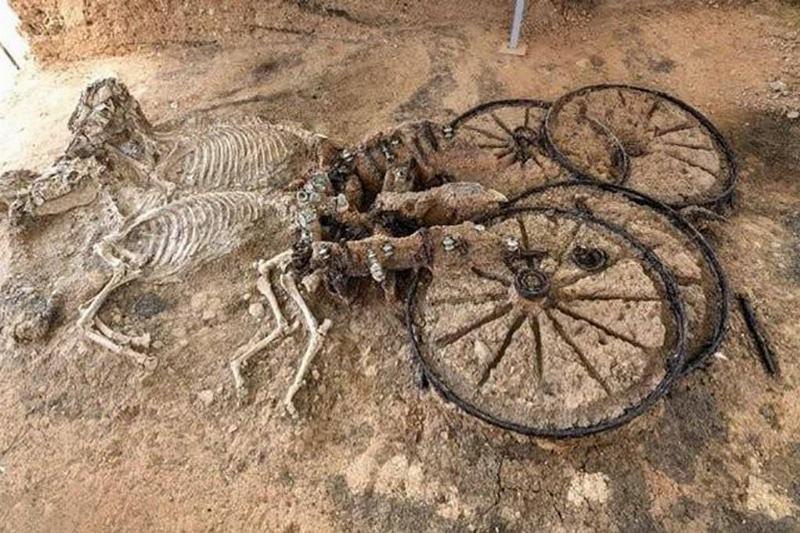
In 2013, archaeologists in Bulgaria discovered an entire carriage connected to two skeletons of horses in the village of Svestari, located in eastern Bulgaria. Incredibly, the carriage still has all four wheels, a seat, a boot, and is believed to have belonged to a member of the Thracian nobility.
ADVERTISEMENT
It’s assumed that the horses became injured falling into a hole and were put out of their misery by the rifer. To many archaeologists, it’s astounding how well preserved the find is.
ADVERTISEMENT
The Safe That Killed A Man
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
Although this may appear to be a regular safe that resulted in the death of the owner, it’s not exactly what one might think. On October 9, 1911, a Tennessee businessman was indeed ironically killed by his own safe. However, there was nothing too strange about it, as all he was doing was trying to retrieve something out of it.
ADVERTISEMENT
When the safe wouldn’t open, he began kicking it, which resulted in a nasty infection on his toe. The infection grew worse and began to spread throughout the rest of his body. The safe was then turned over to his favorite nephew, Lem Motlow, just before the owner died of the infection.
ADVERTISEMENT
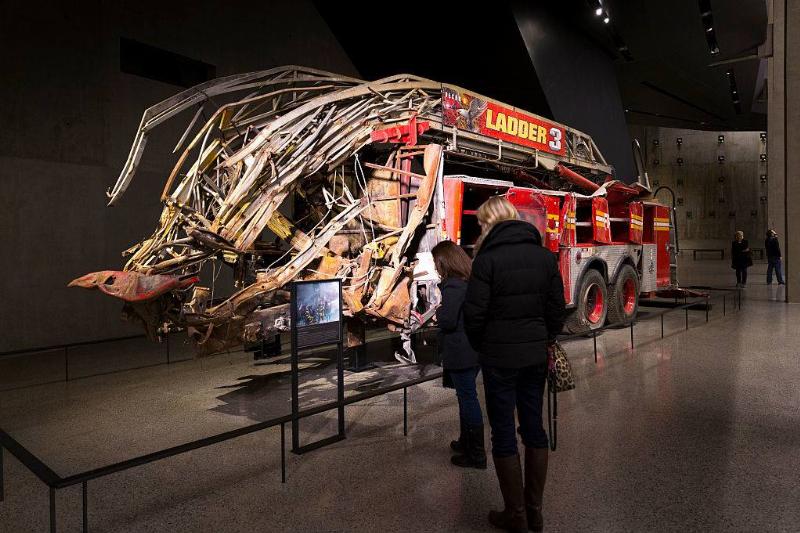
Not An Ordinary Fire Truck
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
Although this may appear to be a fire truck that was involved in some terrible accident, what it actually is is one of the first responders on the morning so September 11, 2001. One piece of the equipment remains at the site in reemergence, which is Ladder 3.
ADVERTISEMENT
This particular truck was driven by Captain Patrick Brown and the rest of his team lost their lives when the North tower collapsed, landing on the truck. After the truck was recovered, it was placed in a hangar at JKF International Airport until it was moved to the Memorial Museum in 2011.
ADVERTISEMENT
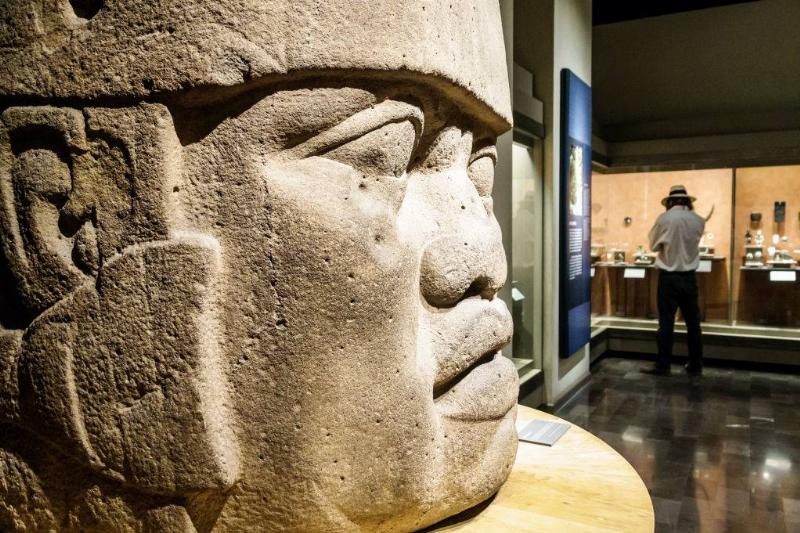
Olmec Warrior Sculptures
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
These massive heads of Olmec sculptures are considered to be some of the most recognizable pieces of tribal art in the world. Incredibly, each is unique and shows the distinctive features of the images that are carved, which provides us with insight into a culture that we still don’t know all that much about.
ADVERTISEMENT
Carved by hand out of a single piece of basalt, it’s incredible how these ancient people managed to move and arrange them at all, considering their weight.
ADVERTISEMENT
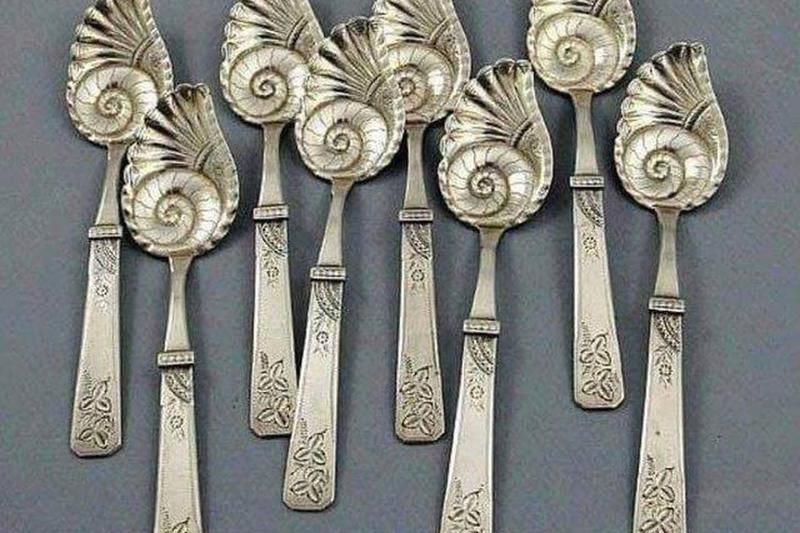
Fancy Spoons For Ice Cream
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
While today, most people might grab any old spoon out of the drawer and dive into a bowl of ice cream, that wasn’t necessarily the case during the Victorian era. Every utensil during that time served a specific purpose, and these particular spoons were used exclusively for ice cream.
ADVERTISEMENT
Although they may seem over-the-top, this was not uncommon for people at the time, and these specials spoons were just right to eat ice cream at the end of the evening.
ADVERTISEMENT
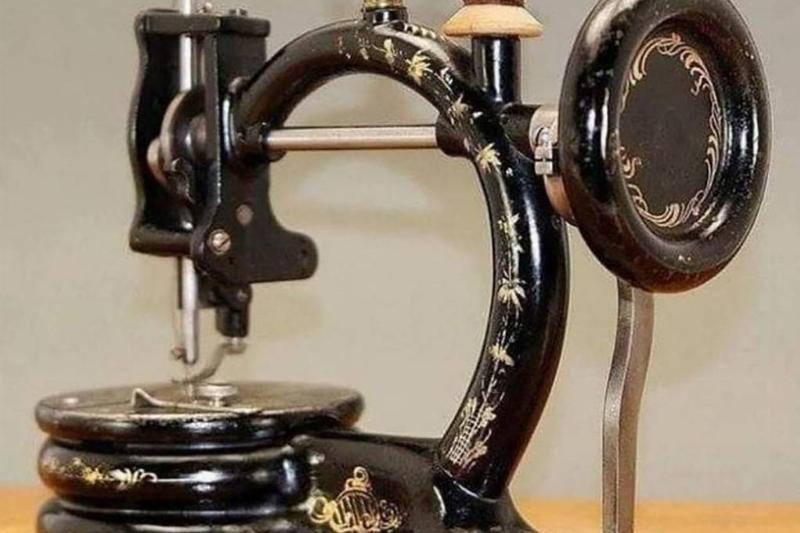
Original Sewing Machine
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
In the years between 1832 and 184, Walter Hunt developed his first sewing machine in his workshop on Amos Street in New York City. The first version of the product was built by hand and contained a curved needle that helped to interlock a stitch over two threads.
ADVERTISEMENT
Over the next 30 years, the machine would be enhanced and bring about a whole new set of possibilities to the fashion industry. At the time of the original sewing machine, there were also plenty of copycat designers looking to make their own original patent, but this was the first.
ADVERTISEMENT
Carbonized Bread
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
To many, this might not seem much more than a loaf of bread but it’s significance is pretty incredible. When the village of Pompeii was destroyed during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 A.D., many people, homes, and artifacts were preserved under a thick blanket of ash.
ADVERTISEMENT
It’s incredible some of the things that managed to be preserved, for example, this loaf of bread. The loaf was so preserved, in fact, that you can still see the baker’s stamp which reads, “Celer, slave of Quintus Granius Verus.”
ADVERTISEMENT
Not Your Typical Halloween Decoration
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
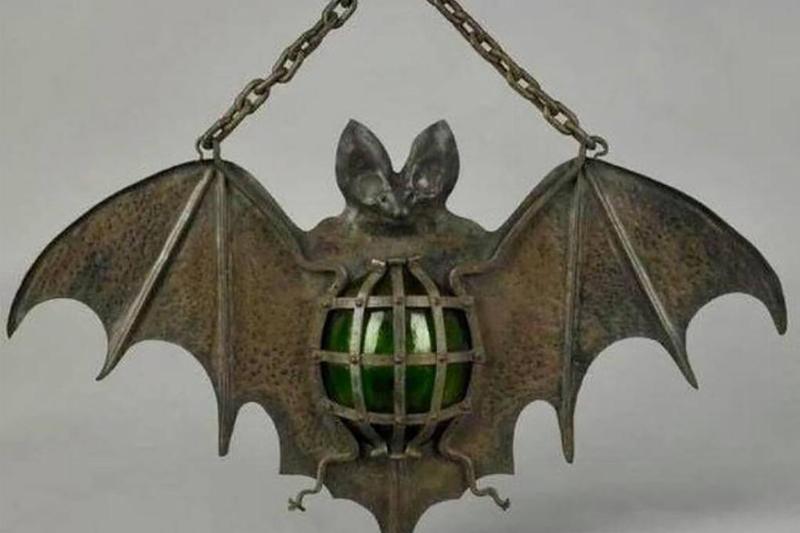
Made of cast iron and shaped like a bat, this lamp was made sometime in the 1930s, and would be the perfect Halloween decoration in today’s culture. However, back when this was made, it’s likely that it was on display year-round, since so much effort when into forging it.
ADVERTISEMENT
Nevertheless, we’re willing to bet that a Halloween enthusiast would pay a pretty penny to have this around their house.
ADVERTISEMENT
Not An Ordinary Ring
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
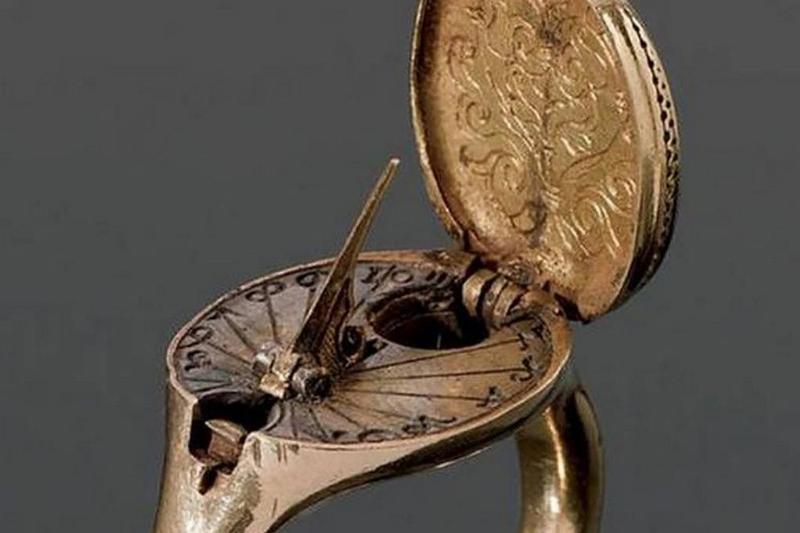
When this ring is closed, it may not look like much more than an ornate gold ring. However, upon opening the top, you’d find that it’s actually a sundial as well.
ADVERTISEMENT
This watch was made back in the 1600s when a sundial was the best bet for a common man to tell the time. So to have one on your finger would have been quite convenient. Furthermore, the ring is also engraved with a coat of arm, which shows that it was probably a family heirloom.
ADVERTISEMENT
Heading Into The Abyss
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
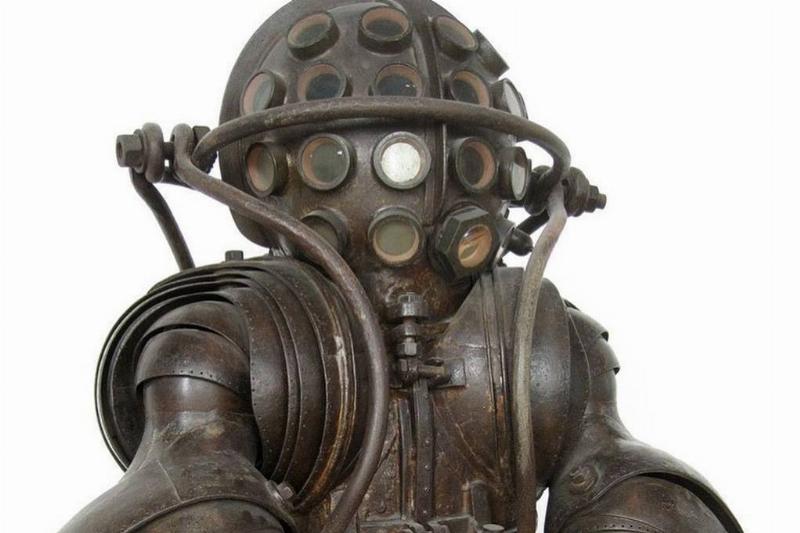
Unbelievably, people have been diving beneath the waves and exploring the deep ocean since at least the Victorian era. Granted, they couldn’t get deep enough without the proper equipment, so they made their own.
ADVERTISEMENT
Pictured above, is a diving suit that was put in use in 1882 and was built by the Carmagnolle brothers of Marseilles, France. The suit had an unbelievable 22 joints and a helmet with 25 individual 2-inch glass viewing points. Unsurprisingly, the suit weighed over 800 pounds.
ADVERTISEMENT
Hearses Aren’t A New Thing
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT

ADVERTISEMENT
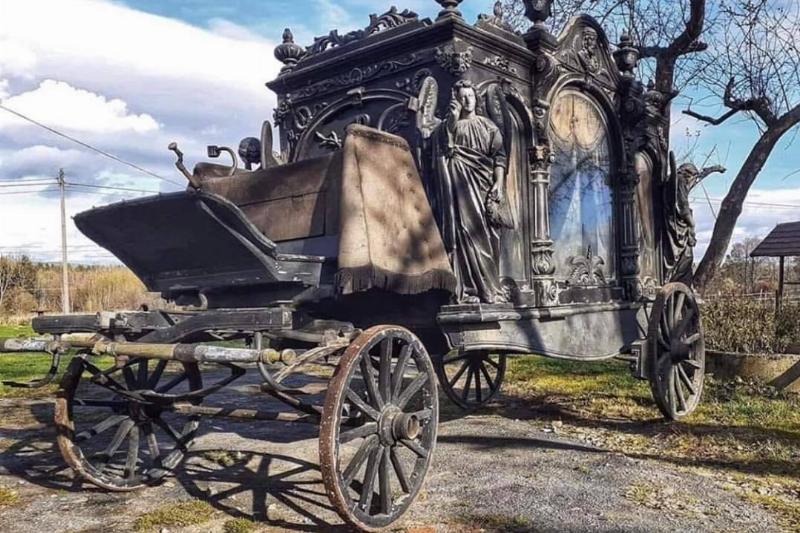
Picturized here is an antique hearse from Dresden, Germany. Although during the Victorian era, there was never any shortage of decoration, this hearse goes above and beyond. Supposedly, the carved angels and arched windows were made specifically for this carriage which makes it even rarer.
ADVERTISEMENT
Although the driver of this carriage remains unknown, it’s clear that anyone riding in this Hearst definitely had some means because this was above the average vehicle to transport a body.



